Last updated on May 13, 2025
The world of entrepreneurship is thrilling, fast-paced, and has its challenges. Being a successful founder requires resilience and support. Entrepreneurs often undertake ventures that do not succeed before creating functional businesses, carving a path of what it takes to build a sustainable company. This guide looks at the key elements that make a successful founder, and helps you to beat the odds.
Why do most startups fail? The answer lies in the data. 42% of startups collapse due to misreading market demand — creating products nobody wants or needs. Others run out of funding (29%), suffer from team issues (23%), or get crushed by competition (19%).
But timing is critical. Launching a startup isn’t just about having a brilliant idea; it’s about introducing that idea at the moment when market conditions, technological capabilities, and consumer needs align.
This comprehensive guide is built for anyone looking to beat the odds – first-time founders seeking a roadmap to success, seasoned entrepreneurs planning their next venture, and investors wanting to spot the next unicorn before everyone else does. We’ve distilled the latest data, expert insights, and proven strategies into actionable steps to help you navigate the startup journey with confidence.
1. Startup Failure Rates: What the Data Says
Understanding why startups fail is perhaps the most crucial first step in ensuring yours succeeds. The statistics paint a clear picture of the challenges that lie ahead for any new business venture.
The Hard Numbers
- 90% of startups fail overall
- 10% fail within the first year
- 70% fail during years two through five
- Failure rates are similar across all industries
The path to startup success is undeniably difficult. It’s widely reported that only one in ten startups survive in the long term. This failure rate has remained surprisingly consistent since the 1990s, suggesting that despite advances in technology and changes in the business landscape, the fundamental challenges of building a successful company remain the same.
First-time founders face particularly steep odds, with only an 18% success rate. Those who have previously failed fare slightly better at 20%, while entrepreneurs who have already built a successful business enjoy the highest odds at 30%.
Why Startups Fail: Breaking Down the Data
The data on why startups fail reveals patterns that every entrepreneur should understand:
- No Market Need (42%): The single biggest reason for startup failure is creating a product that doesn’t solve a real problem for customers. This highlights the critical importance of validating your market before investing significant resources in product development.
- Ran Out of Funding (29%): Cash flow problems sink nearly a third of all startups. In 2023, a staggering 82% of businesses that went under did so because they couldn’t manage their finances effectively.
- Wrong Team (23%): Team issues, including conflicts between founders, skills gaps, or poor hiring decisions, contribute to nearly a quarter of startup failures.
- Outcompeted (19%): Being beaten by competitors is most likely to happen when a startup has been active for three to five years, often just as they’re trying to scale.
- Pricing/Cost Issues (18%): Getting the pricing strategy wrong or miscalculating costs can quickly derail a promising business.
- Poor Product (17%): User-unfriendly products that don’t meet customer expectations lead to high churn rates and eventual failure.
- Poor Marketing (14%): Even great products fail without effective go-to-market strategies.
- Ignoring Customers (14%): Businesses that don’t listen to customer feedback miss crucial opportunities to improve their offerings.
- Product Mistiming (10%): Launching too early or too late can be fatal for startups, highlighting the importance of market timing.
Looking at when startups are most vulnerable, the data shows that while 10% fail in the first year, the highest risk period is between years two and five. This is often when initial funding runs out and businesses must prove sustainable revenue models.
Success Factors: What Sets the 10% Apart
The startups that succeed share certain characteristics:
- Perfect product-market fit: They create solutions that precisely address customer needs
- Comprehensive approach: They don’t ignore any aspect of the business, from product to processes
- Rapid growth: They scale quickly, which attracts further investment
- Adaptable teams: They can pivot and recover from setbacks
Interestingly, startups with co-founders have higher success rates than those with single founders. Having partners creates more accountability and brings complementary skills to the venture.
Industry-Specific Failure Rates
While startup failure rates are generally consistent across sectors, some industries show unique patterns:
- Technology: 63% failure rate within five years (the highest of any industry)
- Construction: Second highest failure rate, with only 36.4% surviving past five years
- Mining: Highest five-year survival rate at 51.3%
- Healthcare: Currently one of the strongest industries for startups, with US healthcare startups bringing in $12.6 billion in revenue in 2022
Understanding these statistics isn’t meant to be discouraging but rather to highlight the importance of preparation, market validation, and financial planning. The most successful entrepreneurs use this knowledge to identify and mitigate risks before they become existential threats to their business.
2. Steps to Launch a Successful Startup
Launching a successful startup requires more than just a brilliant idea. It demands a methodical approach that minimises risk and maximises your chances of creating a sustainable business. Here’s a comprehensive roadmap based on data from successful entrepreneurs.
The Startup Launch Flowchart
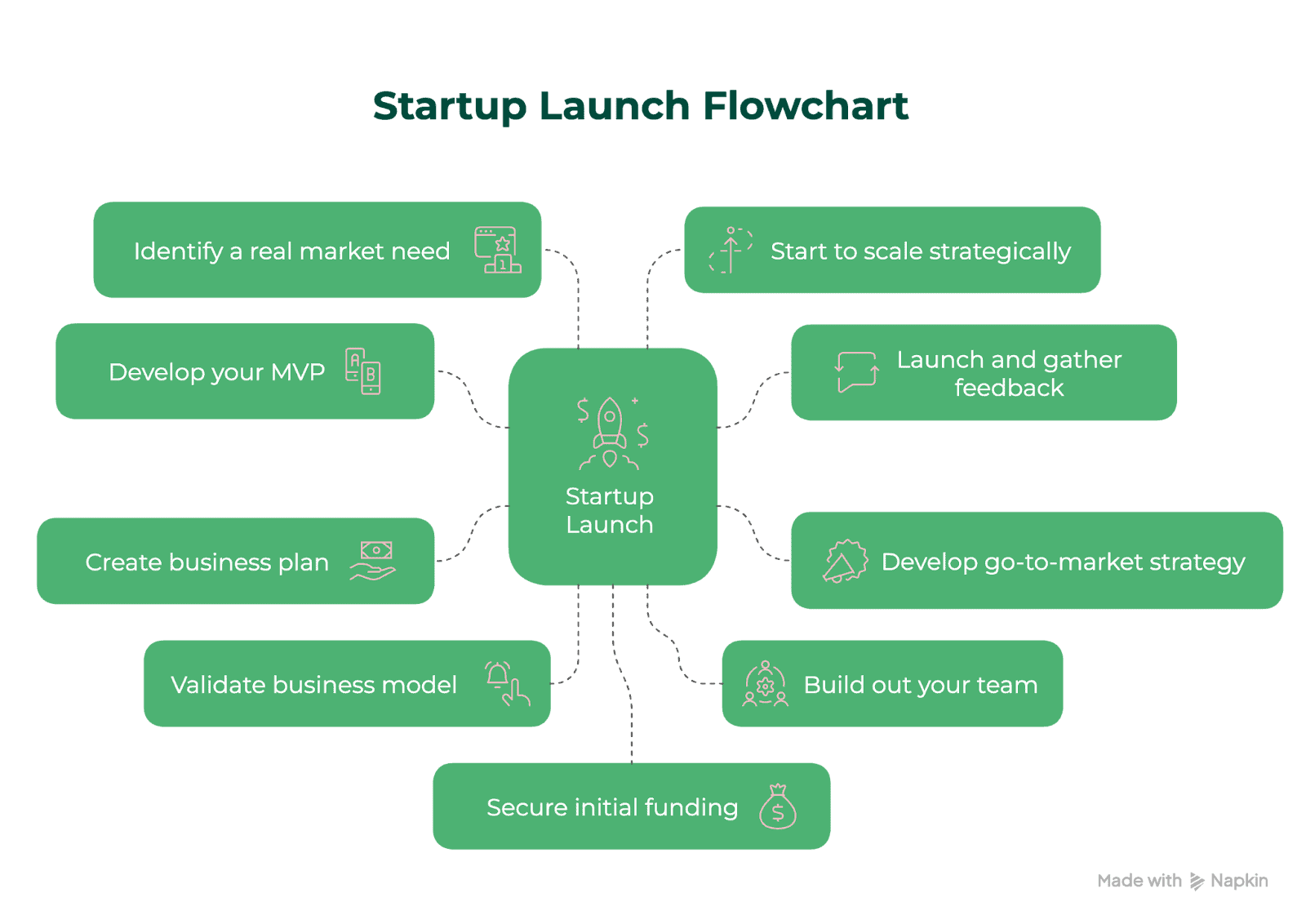
1. Identify a Real Market Need
Remember that 42% of startups fail because they build products nobody wants. Before you invest significant time and resources:
- Conduct thorough market research: Understand your target audience, their pain points, and whether they’re actively seeking solutions
- Evaluate the competition: Identify existing solutions and determine how yours will be substantially better
- Calculate market size: Ensure your target market is large enough to support a scalable business
2. Develop a Minimum Viable Product (MVP)
An MVP allows you to test your core assumptions with minimal investment:
- Focus on core functionality: Build only what’s necessary to solve the primary problem
- Set clear success metrics: Define what constitutes validation before you start building
- Plan for iteration: Your first version will rarely be perfect—build with flexibility in mind
Successful startups typically go through three rounds of funding before reaching Series A, giving them ample opportunity to refine their product based on market feedback.
3. Validate Your Business Model
With your MVP in hand, it’s time to confirm that customers will pay for your solution:
- Get real user feedback: Put your product in front of actual potential customers
- Measure engagement metrics: Look at how users interact with your product
- Test pricing strategies: Experiment to find the optimal price point
- Calculate unit economics: Ensure your business model is profitable at scale
Only 2 in 5 startups are profitable, while 1 in 3 break even, and 1 in 3 continue to lose money. Validating your business model early helps ensure you end up in the first group.
It’s important to note that in deeptech and climatetech sectors, the path to profitability is often longer and more capital-intensive due to significant upfront R&D investment, extended development cycles, and complex regulatory or policy environments-meaning that demand may be generated while the technology is still being developed, and macroeconomic or policy factors can heavily influence when (or if) profitability is reached
4. Create a Comprehensive Business Plan
A solid business plan serves as your roadmap and is essential for securing funding:
- Executive summary: Concise overview of your business concept
- Market analysis: Detailed breakdown of your target market and competition
- Product/service description: Clear explanation of your offering and its unique value
- Marketing strategy: How you’ll acquire and retain customers
- Operational plan: Day-to-day running of the business
- Financial projections: Realistic forecasts for at least three years
- Funding requirements: How much capital you need and how you’ll use it
Entrepreneurs who create detailed business plans are 16% more likely to succeed than those who don’t, according to research from the Harvard Business Review.
5. Secure Initial Funding
Before approaching external investors, consider these funding sources:
- Personal savings: 31% of employer firms start with less than £10,000
- Friends and family (“love money”): The most popular funding method for startups in 2023
- Business loans: Along with credit cards and lines of credit, these account for about 75% of financing for new firms
- Grants and competitions: Non-dilutive funding available in many industries
- Angel investors: Individual investors who typically invest between £25,000 and £500,000
Calculate your startup costs carefully. The average startup with five employees spends around £300,500 on payroll in the first year, with equipment costs ranging from £10,000 to £125,000 depending on your industry.
6. Build Your Team
Team issues contribute to 23% of startup failures, making hiring decisions crucial:
- Identify key roles: Determine which positions are essential for your specific business
- Seek complementary skills: Look for team members whose abilities fill gaps in your own expertise
- Consider co-founders: Startups with co-founders have higher success rates than solo ventures
- Assess cultural fit: Ensure new hires align with your company values
- Plan for growth: Build a team that can scale with your business
It takes an average of six months to hire someone for a startup, so start the recruitment process well in advance of your needs.
7. Develop a Go-to-Market Strategy
Poor marketing contributes to 14% of startup failures. Your go-to-market strategy should include:
- Customer acquisition channels: Where and how you’ll find your first customers
- Messaging and positioning: How you’ll communicate your value proposition
- Launch timeline: Sequenced steps for introducing your product to the market
- Success metrics: KPIs to measure the effectiveness of your launch
- Budget allocation: How you’ll invest in your marketing resources
According to Forbes, the time of year you pitch, the detail of your data, and the value of your pitch deck are among the strongest factors affecting the amount of funding a business receives.
8. Launch and Gather Feedback
Once you’re in the market:
- Implement feedback loops: Create systems to collect and analyse user feedback
- Monitor key metrics: Track the performance indicators that matter most for your business
- Iterate quickly: Make improvements based on real-world usage
- Optimise conversion funnels: Identify and address drop-off points in your customer journey
The most successful startups continually refine their offering based on user feedback, often making significant pivots in their early years.
9. Scale Strategically
Scaling too early is a common mistake. Before scaling:
- Ensure product-market fit: Confirm strong customer demand and satisfaction
- Optimise unit economics: Make sure you’re profitable on a per-customer basis
- Build repeatable processes: Develop systems that can handle increased volume
- Secure growth capital: Raise the funding needed to support expansion
Research showed that inconsistent startups that scale prematurely generate three times more capital during the efficiency stage but 18 times less capital during the scale stage compared to consistent startups.
By following these steps and being methodical in your approach, you can significantly increase your odds of building a startup that survives and thrives beyond the critical five-year mark.
3. Startup Funding Trends (2025)
The funding landscape for startups continues to evolve, with significant shifts in investment preferences, funding amounts, and investor expectations. Understanding these trends is crucial for founders looking to secure capital in today’s competitive environment.
Current Funding Environment
The venture capital market has seen substantial growth over the past decade, reaching a record £200 billion in 2022. However, the funding environment remains highly competitive, with venture capital firms receiving more than 1,000 proposals per year while typically focusing on businesses requiring at least £250,000 in investment.
Funding Rounds: Timelines and Expectations

Securing funding takes time, and founders should plan accordingly:
- Pre-seed to Seed: Typically self-funded or raised from friends, family, and angel investors
- Seed to Series A: Average time between these rounds is 18 months
- Series A to Series B: Typically takes 10-18 months
- Series B to Series C: Average time between these rounds is 27 months
Funding Amounts by Stage
Funding amounts vary significantly by stage, with recent data showing:
- Seed: Average of £500,000 to £2 million
- Series A: Average of £15 million in 2022, up from £12.1 million in 2017
- Series B: Typically between £20-30 million
- Series C: Average of £68 million
Notably, 47% of Series A startups spend £400,000 or more per month, highlighting the importance of raising sufficient capital to sustain operations between funding rounds.
Investor Focus Areas for 2025
Certain sectors are attracting disproportionate investor interest:
Healthcare:
- Healthcare accounted for 16.5% of global VC deal activity in Q1 2025.
- Digital health startups secured $10.1 billion in venture funding in 2024.
- Key drivers include AI-driven innovation, biotechnology, and operational efficiency, with a surge in M&A and IPO activity expected this year.
Fintech:
- Private fintech company financing reached nearly $14 billion in Q1 2025, a 50% year-over-year increase.
- M&A activity hit record highs, with 437 transactions totaling $56 billion in Q1 alone.
- Early-stage investment remains strong, and major IPOs are anticipated, although some have been delayed due to market volatility.
AI and Machine Learning
- The AI industry is projected to reach $243.7 billion in 2025.
- AI is increasingly integrated across sectors, especially in healthcare, fintech, and enterprise software.
- Major funding rounds and rapid adoption are fueling continued growth, despite high startup failure rates.
Climate Tech
- Investors hold an estimated $86 billion in available capital (“dry powder”) for climate tech in 2025.
- The focus is shifting to commercially viable, scalable solutions rather than those relying on a “green premium.”
- Key growth areas include AI-powered climate solutions, advanced power management, earth observation, and adaptation technologies (e.g., wildfire detection, energy storage).
Crypto and Blockchain
- Crypto startups raised $5.85 billion in Q1 2025, already accounting for 61% of all 2024 capital raised.
- Institutional investor hesitancy persists, but project-level investment is regaining momentum, especially in areas like CeFi, blockchain infrastructure, and real-world asset tokenisation.
Gender Disparities in Funding
Significant disparities persist in how funding is distributed:
- In 2022, founders who are men brought in £156.2 billion in venture capital
- Women founders raised just £28.1 billion in the same period
This disparity highlights ongoing challenges for women entrepreneurs seeking funding.
Alternative Funding Sources
Beyond traditional venture capital, startups are increasingly turning to alternative funding sources:
- Crowdfunding: the total value of crowdfunding reached £1.06 billion in 2023
- Revenue-based financing: Growing in popularity for companies with predictable revenue
- Venture debt: Large unicorn startups like Airbnb and Uber have taken on billions in debt to fuel growth
- Corporate venture capital: Established companies investing in startups for strategic advantages
Unicorn Trends
The unicorn landscape (startups valued at over $1 billion) continues to expand:
- In 2022, there were 1,000 “active unicorns” in the US collectively worth £1.1 trillion.
- The US accounts for slightly more than half (53.9%) of all unicorns globally.
- The UK is the leading unicorn hub in Europe, and ranks 4th globally after the US, China, and India, with 53 unicorns as of early 2025 collectively valued at around $172b.
- 80% of the UK’s unicorns and soonicorns are based in London.
- Across Europe, there are 514 unicorn startups spread across 65 cities.
- Only about 1% of startups ever achieve unicorn status.
Funding Success Factors
What makes investors say yes? Research points to several key factors:
- Team quality and experience: Founders with successful track records have a 30% chance of success with their next venture, compared to 18% for first-timers.
- Market timing: Aligning your product or service with emerging customer needs and industry trends can significantly improve your odds of attracting investor interest and achieving product-market fit.
- Pitch quality: The detailedness of data and the value of the pitch deck significantly impact funding success
- Traction metrics: Demonstrable market validation and growth
- Unit economics: Clear path to profitability
Understanding these funding trends and preparing accordingly can significantly increase your chances of securing the capital needed to grow your startup. Remember that the average time between funding rounds gives you a limited runway, so planning your capital needs carefully is essential for survival.
4. Startup Team Structure & Roles
Building the right team is a critical factor in startup success, with team issues contributing to 23% of startup failures. The composition, structure, and dynamics of your founding team can make or break your venture, particularly in the early stages.
The Ideal Founding Team
Research shows that team composition significantly impacts startup outcomes:
- Two founders increase success odds: Startups with two founders see 30% more investment, three times the customer growth rate, and are less likely to scale too quickly
- Complementary skills matter: Successful teams combine different but complementary expertise
- Experience alone isn’t enough: Harvard Business Review research indicates that “entrepreneurial passion” and “shared strategic vision” are as important as technical skills
- Age diversity helps: Contrary to the stereotype of young founders, a 2023 study showed that a 60-year-old is three times as likely to build a successful startup as a 30-year-old
Common Startup Roles and Responsibilities
As your startup grows, you’ll need to establish clear roles and responsibilities. Here’s a breakdown of key positions and their typical salaries:
| Role | Responsibilities | Average Salary (£) |
|---|---|---|
| CEO (Chief Executive Officer) | Overall strategy, fundraising, team building | 100,000 – 150,000 |
| CTO (Chief Technology Officer) | Technical vision, architecture, development leadership | 90,000 – 130,000 |
| CMO (Chief Marketing Officer) | Brand strategy, marketing initiatives, customer acquisition | 85,000 – 120,000 |
| CFO (Chief Financial Officer) | Financial planning, investor relations, cash flow management | 90,000 – 140,000 |
| COO (Chief Operating Officer) | Day-to-day operations, process optimisation, team management | 85,000 – 130,000 |
| Product Manager | Product roadmap, feature prioritisation, market research | 60,000 – 90,000 |
| UX/UI Designer | User experience, interface design, usability testing | 45,000 – 75,000 |
| Software Engineer | Code development, technical implementation, debugging | 50,000 – 100,000 |
| Sales Director | Sales strategy, team leadership, revenue growth | 70,000 – 110,000 |
| Customer Success Manager | User onboarding, retention, satisfaction | 40,000 – 70,000 |
Note: Salary ranges vary by location, industry, company stage, and individual experience. Many early-stage startups offer lower cash compensation supplemented with equity.
When to Hire for Each Role
Timing your hires appropriately is crucial for managing burn rate and ensuring you have the right capabilities at each stage:
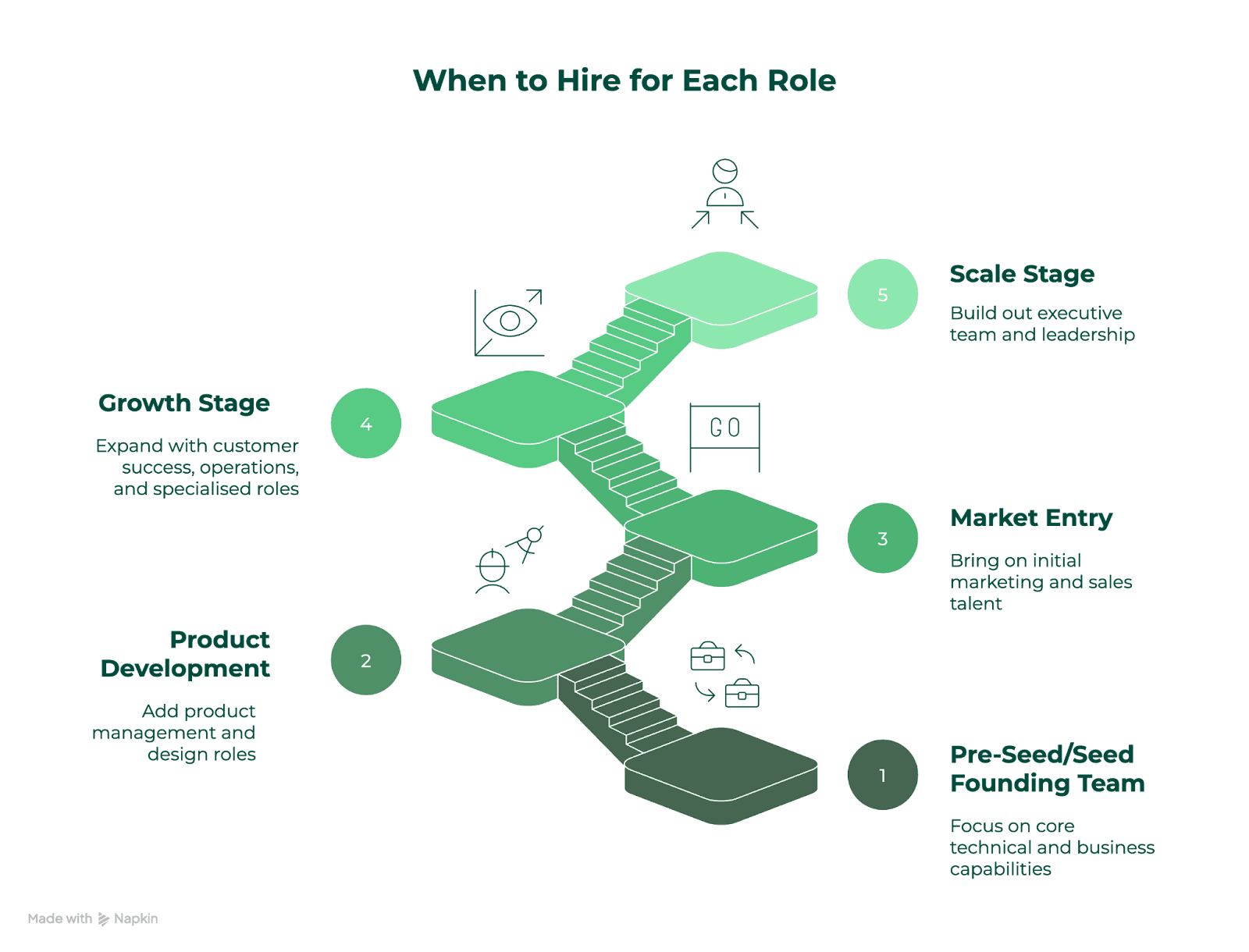
Team Structure Evolution
As startups grow, their org charts evolve:
- 1-5 employees: Flat structure, everyone does everything
- 6-15 employees: Informal functional divisions begin to emerge
- 16-50 employees: Formal departments with managers
- 51-100 employees: Multiple layers of management, specialised roles
- 100+ employees: Structured hierarchy, established processes
Interestingly, data shows that startup failure is most common when the company has 11-50 employees — a critical transition period where governance and communication structures must evolve.
Outsourcing vs. In-house
Strategic decisions about which functions to keep in-house and which to outsource can help manage costs:
- 66% of small businesses outsource services to other small businesses
- Startup owners spend around 40% of their working hours on tasks that don’t generate income (hiring, HR, payroll)
- Common outsourced functions include accounting, legal, HR administration, and specialised marketing
Building Resilient Teams
The ability to recover from setbacks is a hallmark of successful startup teams:
- Teams need a growth mindset that views challenges as opportunities
- Regular feedback mechanisms help address issues before they escalate
- Clear communication channels ensure alignment during pivots
- Shared values and mission help maintain cohesion during difficult periods
Building the right team is not just about hiring people with the right skills—it’s about creating a group with the right dynamics, shared vision, and complementary capabilities.
5. Top Startup Industries in 2025
The startup ecosystem is constantly evolving, with new industries emerging and others transforming as technology and market demands shift. Based on current data and projections, here are the top startup industries showing the most promise in 2025.
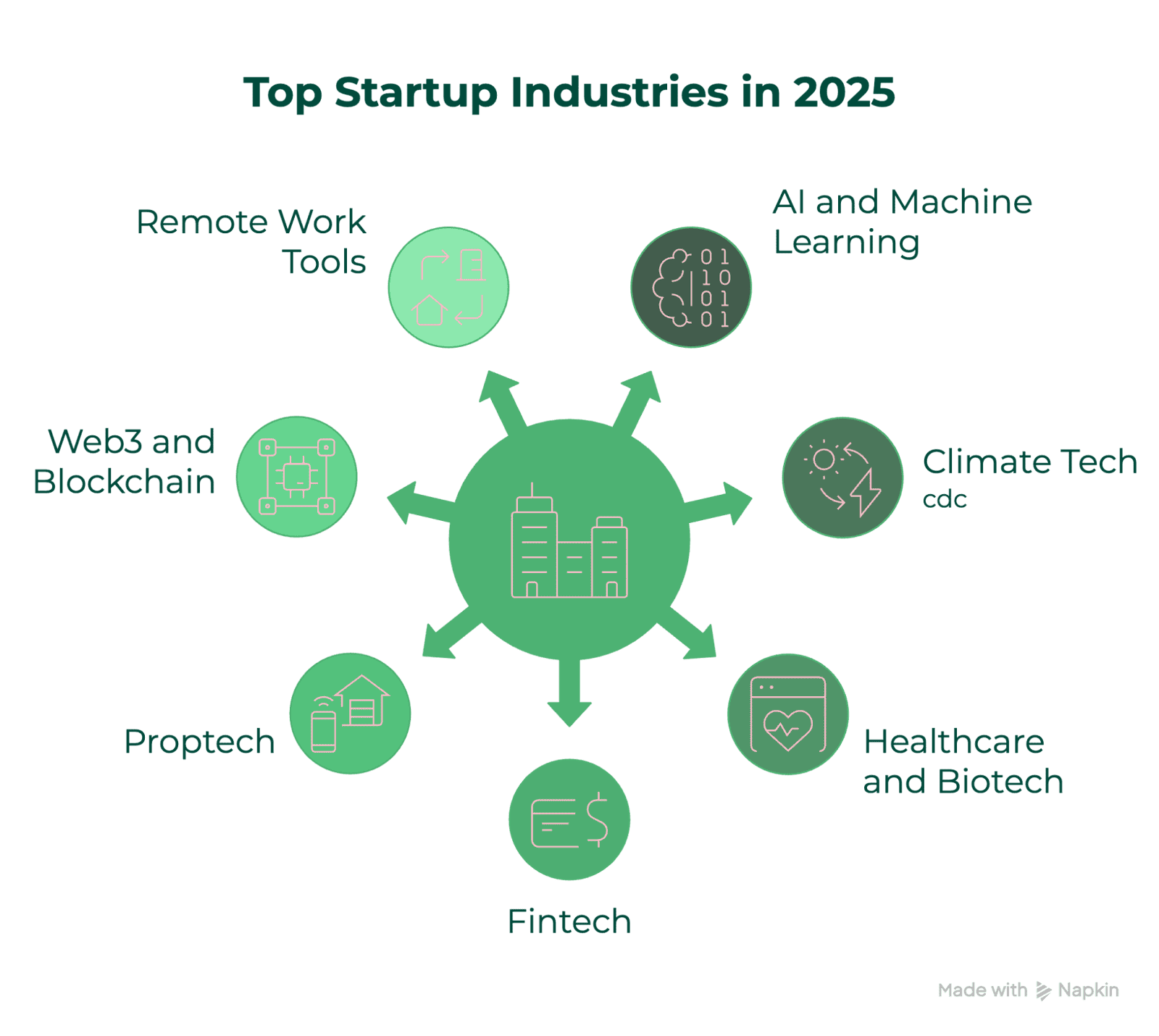
AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence continues to revolutionise virtually every sector, creating abundant opportunities for startups:
- The global AI market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 37.3% from 2023 to 2030
- AI-driven startups are attracting significant venture capital despite predictions that 85% will fail in their first three years
- Key niches include:
- Generative AI applications for content creation and design
- AI-powered automation for business processes
- Machine learning solutions for healthcare diagnostics
- Computer vision for autonomous systems
- Natural language processing for customer service and content analysis
Success stat: AI technology is estimated to boost profits by 71% for companies in the construction industry alone.
Climate Tech and Sustainability
With environmental concerns becoming increasingly urgent, climate tech startups are seeing rapid growth:
- Global investment in climate tech reached £75 billion in 2023
- Growth areas include:
- Renewable energy solutions
- Carbon capture and offset technologies
- Sustainable agriculture and food systems
- Circular economy platforms
- Climate risk assessment and management tools
Success stat: Climate tech startups with clear metrics for carbon reduction or resource conservation are 2.3x more likely to secure Series A funding.
Healthcare and Biotech
Healthcare innovation continues to attract substantial investment:
- In 2024, US digital health startups raised $10.1 billion across 497 deals.
- UK healthtech and life sciences startups raised £1.4 billion in venture capital investment in Q1 2025 alone. While direct UK startup revenue figures are less public, the NHS presents significant opportunities for innovation-especially in digital health, AI-driven diagnostics, and patient workflow solutions.
- Promising subsectors include:
- Digital health platforms and telemedicine
- Precision medicine and personalised healthcare
- Mental health technologies
- Medical device innovations
- Healthcare AI diagnostics
Success stat: Healthcare startups have a 15% higher five-year survival rate compared to the average across all industries.
Fintech
Financial technology remains a hot sector, with continuous disruption of traditional banking and financial services:
- Private fintech company financing reached nearly $14 billion in Q1 2025, a 50% year-over-year increase.
- Emerging areas include:
- Decentralised finance (DeFi) applications
- Embedded finance solutions
- Regulatory technology (RegTech)
- Insuratech innovations
- Financial inclusion platforms for underserved markets
Success stat: About 80% of financial institutions have implemented a fintech partnership, creating significant opportunities for B2B fintech startups.
Proptech (Real Estate Technology)
Technology is transforming how properties are bought, sold, managed, and developed:
- In 2024, proptech startups globally raised approximately $15.1 billion from venture capital investors
- Growing niches include:
- AI-powered real estate platforms
- Smart building technologies
- Property management software
- Virtual and augmented reality for property viewing
- Fractional ownership platforms
Success stat: Residential real estate startups using artificial intelligence tools are bringing in the most investments, with companies like Zillow securing £565 million in funding.
Web3 and Blockchain
Despite crypto market volatility, underlying blockchain technology continues to advance:
- Crypto startups raised approximately $13.6 billion globally from venture capital investors in 2024.
- Promising areas include:
- Enterprise blockchain solutions
- Decentralised autonomous organisations (DAOs)
- Web3 infrastructure
- Tokenisation platforms
- Blockchain for supply chain transparency
Success stat: The most recent data shows that 28% of American adults-about 65 million people-own cryptocurrency as of early 2025
Remote Work and Collaboration Tools
The shift to flexible work arrangements continues to create opportunities:
- The global market for collaboration software is expected to reach £35 billion by 2026
- Growth areas include:
- Virtual office environments
- Asynchronous collaboration tools
- Project management platforms for distributed teams
- HR tech for remote workforces
- Team culture and wellness solutions
Success stat: Companies offering remote work tools with built-in analytics experienced 40% faster growth during 2022-2023.
Industry-Specific Success Factors
Different industries have varying success rates and funding patterns:
- Technology: While the tech startup industry has the highest failure rate at 63%, it also produces the most unicorns
- Healthcare: One of the most resilient sectors, particularly for solutions addressing preventative care and chronic disease management
- Fintech: Success often depends on strategic partnerships with established financial institutions
- Climate Tech: Startups with clear impact metrics and regulatory advantages show stronger performance
For entrepreneurs choosing an industry to enter, these insights suggest that while technology-driven ventures offer the highest upside, they also come with the greatest risk. Industries with clear regulatory tailwinds (like climate tech) or established partnership models (like healthcare and fintech) may offer more predictable paths to success.
6. Tools & Platforms Every Startup Needs
In today’s digital landscape, the right tech stack can be the difference between efficiency and chaos for a growing startup. Here’s a comprehensive overview of essential tools and platforms to power your venture across different functional areas.
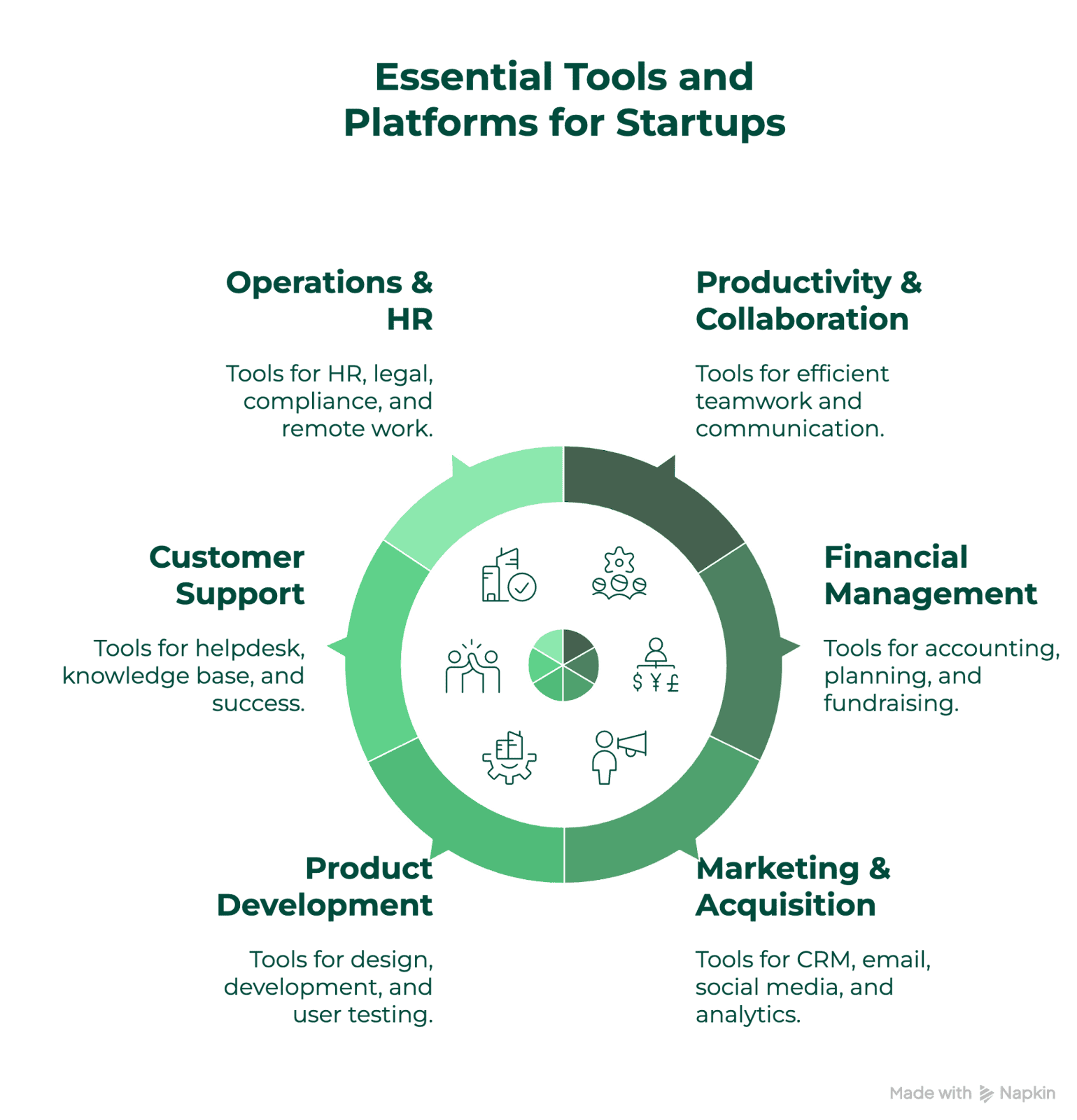
Productivity & Team Collaboration
These tools help teams work together efficiently, regardless of location:
- Project Management:
- Asana: Visual project tracking with customisable workflows
- Monday.com: Flexible work management platform
- ClickUp: All-in-one productivity platform with docs, goals, and tasks
- Trello: Kanban-style project boards for visual organisation
- Team Communication:
- Slack: Channel-based messaging with robust integrations
- Microsoft Teams: Communication platform with deep Office 365 integration
- Discord: Voice, video, and text communication platform popular with tech teams
- Document Collaboration:
- Google Workspace: Cloud-based docs, sheets, slides, and storage
- Coda: Flexible document platform that combines docs, spreadsheets, and applications
Financial Management
Managing finances effectively is crucial, with cash flow problems contributing to 29% of startup failures:
- Accounting & Bookkeeping:
- Xero: Cloud accounting software for small businesses
- QuickBooks: Comprehensive accounting solution with payroll options
- FreshBooks: Invoicing and accounting for service-based businesses
- Financial Planning:
- Runway: Cash flow forecasting and scenario planning
- Pulse: Real-time cash flow management
- Brex: Business account with built-in expense management
- Fundraising & Equity:
- Carta: Cap table and equity management
- DocSend: Secure document sharing with investor analytics
- PitchBook: Private market data for investor research
Marketing & Customer Acquisition
With poor marketing contributing to 14% of startup failures, these tools are essential:
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM):
- HubSpot: All-in-one marketing, sales, and service platform with free starter tier
- Pipedrive: Sales-focused CRM with visual pipeline management
- Zoho CRM: Customisable CRM with automation capabilities
- Email Marketing:
- Mailchimp: Email marketing platform with automation and landing pages
- ConvertKit: Creator-focused email marketing tool
- Klaviyo: E-commerce focused email marketing with advanced segmentation
- Social Media & Content:
- Buffer: Social media scheduling and analytics
- Canva: Graphic design platform for marketing materials
- Ahrefs: SEO research and content planning tools
- Analytics:
- Google Analytics: Web traffic and user behavior tracking
- Mixpanel: Product analytics for user engagement
- Hotjar: Heatmaps and user recordings for UX optimisation
Product Development
Building user-friendly products is critical, as poor products account for 17% of startup failures:
- Design & Prototyping:
- Figma: Collaborative interface design tool
- Adobe XD: UI/UX design and prototyping
- InVision: Interactive prototypes and design collaboration
- Development & Deployment:
- GitHub: Code repository and version control
- Jira: Agile development project management
- CircleCI: Continuous integration and delivery platform
- User Testing & Feedback:
- UserTesting: Remote user testing platform
- Maze: Rapid testing platform for digital products
- SurveyMonkey: Custom surveys for user feedback
Customer Support & Success
Ignoring customers leads to 14% of startup failures, making these tools valuable:
- Helpdesk & Support:
- Zendesk: Customer service platform with ticketing system
- Intercom: Conversational relationship platform for support and engagement
- Help Scout: Customer support platform with shared inbox
- Knowledge Base:
- Notion: Customisable knowledge base creation
- Slite: Team wiki and documentation platform
- Document360: Purpose-built knowledge base software
- Customer Success:
- ChurnZero: Customer success platform to reduce churn
- Gainsight: Customer success management software
- Totango: Customer success platform with health scoring
Operations & HR
Running efficient backend operations is essential for scaling:
- HR & Payroll:
- Gusto: All-in-one HR platform for payroll, benefits, and onboarding
- BambooHR: HR software for managing employee data
- Rippling: Employee management platform for IT and HR
- Legal & Compliance:
- Clerky: Legal automation for startups
- DocuSign: Electronic signature and agreement management
- Founders Law Store: Browse premium legal document templates and bundles tailored to your needs.
- Remote Work:
- Deel: Global payroll and compliance for remote teams
- Remote: International payroll, benefits, and compliance
- Workfrom: Virtual office platform for remote teams
Choosing the Right Tools
When building your startup’s tech stack:
- Start lean: Begin with essential tools and add more as you grow
- Consider integrations: Choose tools that work well together
- Factor in scalability: Select platforms that can grow with your business
- Balance cost and functionality: Free tiers can work initially, but plan for upgrades
- Prioritise security: Ensure tools meet your data protection requirements
According to a recent survey, 92% of business owners believe that having the right digital tools is the most effective strategy for startup success. By thoughtfully selecting platforms that align with your specific needs, you can increase efficiency, reduce costs, and create a foundation for sustainable growth.
7. Case Studies: What Worked and What Didn’t
Learning from both successes and failures provides invaluable insights for aspiring entrepreneurs. These case studies highlight key lessons from startups that navigated the challenges of building a business — some successfully, others not.
Success Story: Figma
Founded: 2012
Founders: Dylan Field and Evan Wallace
Industry: Design Software
Current Status: Acquired by Adobe for $20 billion in 2022
The Journey: Figma began with a bold vision to make design accessible to everyone by creating a browser-based collaborative design tool. The founders identified a key gap in the market: existing design tools were siloed, expensive, and didn’t allow for real-time collaboration.
Key Success Factors:
- Perfect Product-Market Fit: Figma addressed a real pain point for design teams who needed to collaborate remotely.
- Strategic Patience: The team spent four years in development before launching, ensuring the technology was rock-solid.
- Freemium Business Model: Their free tier created massive adoption among students and small teams, who later converted to paid plans as they grew.
- Community Focus: Figma built a thriving community around their product, hosting events and creating educational content.
- Timing Advantage: The rise of distributed teams and remote work created ideal market conditions for their solution.
Metrics That Matter:
- Grew to 4 million users before acquisition
- 86% of users reported increased productivity
- Achieved profitability before their Series C funding round
- Built a diverse team with 40% women employees
Takeaway: Figma’s success demonstrates the power of solving a genuine market need with a superior product and patient, community-focused growth strategy.
Success Story: Stripe
Founded: 2010
Founders: Patrick and John Collison
Industry: Fintech/Payments
Current Status: Valued at $95 billion in 2021
The Journey: Irish brothers Patrick and John Collison founded Stripe to solve a seemingly simple problem: making it easier for websites to accept payments. What set them apart was their laser focus on developer experience, creating an API that could be implemented with just a few lines of code.
Key Success Factors:
- Developer-First Approach: By focusing on making their product irresistible to developers, Stripe created a powerful adoption channel
- Continuous Iteration: Relentless improvement of their core product while expanding the ecosystem
- Strategic Expansion: Methodical addition of features and geographic markets
- Strong Culture: Building a world-class team with a clear mission and values
- User-Centric Documentation: Setting the gold standard for technical documentation and support
Metrics That Matter:
- Processing billions in payments annually for millions of businesses
- 14 global offices across 40+ countries
- 90%+ of American adults have purchased from a business using Stripe
- Consistently rated among the best places to work in tech
Takeaway: Stripe demonstrates how deeply understanding user needs (in their case, developers) and executing flawlessly on a simple but powerful value proposition can create extraordinary growth.
Patterns of Success
Analysing these case studies reveals consistent patterns:
Success Patterns:
- Deep understanding of user needs: Successful startups solve genuine problems
- Disciplined growth: Scaling after proving product-market fit and unit economics
- Adaptability: Willingness to pivot based on market feedback
- Capital efficiency: Making every dollar count, especially in early stages
- Strong culture: Building teams aligned with the company’s mission
These case studies reinforce the statistics presented earlier: successful startups combine the right product, the right market, and the right execution—all at the right time. While having experienced founders, adequate funding, and innovative technology all contribute to success, they cannot overcome fundamental flaws in the business model or significant disconnects with market demand.
8. Key Takeaways + Startup Kit
After exploring the data, strategies, and real-world examples throughout this guide, we’ve distilled the most crucial insights into actionable takeaways for aspiring and current founders. Use these principles to navigate your startup journey with greater confidence and higher odds of success.
Essential Startup Success Principles
- Validate market need before building: Remember that 42% of startups fail because they build products nobody wants. Conduct thorough customer discovery and market research before investing significant resources.
- Focus on sustainable unit economics: Ensure your business model works at the individual customer level before scaling. Businesses with positive unit economics can survive downturns and funding droughts.
- Build the right team: Startups with complementary co-founders have a 30% higher success rate. Look for team members who bring diverse skills and shared values.
- Plan your funding runway carefully: With the average time between Seed and Series A being 18 months, ensure you have sufficient capital to reach key milestones before you need to raise again.
- Embrace data-driven iteration: Successful startups continuously refine their products based on user feedback and metrics, often making significant pivots in their early years.
- Manage cash flow meticulously: 82% of businesses that went under in 2023 did so because of cash flow problems. Monitor your burn rate and maintain at least 6-12 months of runway.
- Time your market entry strategically: Product mistiming accounts for 10% of startup failures. Launch when the market is ready, not too early or too late.
- Scale only after proving product-market fit: Premature scaling is a common killer of promising startups. Focus on retention and customer satisfaction before aggressive growth.
- Select the right tools and infrastructure: 92% of business owners believe having the right digital tools is critical to startup success. Build a tech stack that can grow with your business.
- Prepare for the long haul: The startup journey typically takes longer than expected. Research shows that entrepreneurs consistently underestimate market validation time by a factor of 3x.
Final Thoughts: Embracing Both Data and Intuition
While this guide has emphasised data-driven decision making, successful entrepreneurship also requires intuition, creativity, and resilience. The statistics show that 90% of startups fail, but they don’t determine whether yours will be among them.
As Matthew Scullion, Founder of Matillion, put it: “Start. Then don’t stop. The biggest killer of businesses is not starting. The second biggest is quitting. The second thing is to act like you’re building something huge. Assume from day one you’re building a billion-dollar business, then behave accordingly.”
By combining the hard-won lessons from those who have gone before you with your unique vision and determination, you can navigate the challenging but rewarding journey of building a successful startup. Remember that every unicorn company was once a fledgling startup facing the same daunting statistics you now confront.
The difference between the 90% that fail and the 10% that succeed often comes down to preparation, timing, execution, and yes — a measure of good fortune. But by applying the principles and tools in this guide, you significantly tilt those odds in your favor.
We at Founders Forum Group are excited to support you on this journey. Reach out to our community for mentorship, connections, and further resources as you build the next generation of world-changing companies.
This guide is updated annually with the latest statistics and trends. For additional resources and support, visit the Founders Forum Group website or join our community events.
Sources:
British Business Bank. (2023). Small Business Finance Markets Report 2023.
https://www.british-business-bank.co.uk/research/sbfm
Burke, A., Fraser, S., & Greene, F.J. (2010). The Multiple Effects of Business Planning on New Venture Performance. Journal of Management Studies, 47(3), 391–415.
CB Insights. (2023). Startup Failure Post-Mortems.
https://www.cbinsights.com/research/startup-failure-post-mortem
CB Insights. (2024). The Top 12 Reasons Startups Fail.
https://www.cbinsights.com/research/report/startup-failure-reasons-top
CB Insights. (2025). State of Fintech Q1 2025 Report.
https://www.cbinsights.com/research/report/fintech-trends-q1-2025
CRETI. (2024). 2024 Proptech Venture Capital Analysis.
https://www.creti.org/insights/2024-proptech-venture-capital-analysis
Crunchbase. (2023). Funding to Female Founders 2023.
https://about.crunchbase.com/blog/female-founder-funding-2023
Crunchbase. (2024). Startup Funding Stages and Timelines.
https://about.crunchbase.com/blog/startup-funding-stages
Crunchbase. (2025). Crypto Funding Report Q1 2025.
https://news.crunchbase.com/crypto-q1-2025-funding
Dealroom. (2024). Startup Funding Rounds and Benchmarks 2024.
https://dealroom.co/resources/reports/startup-funding-benchmarks-2024
Forbes. (2024). How to Pitch Your Startup and Raise Capital in 2024.
Harvard Business Review. (2017). How to Write a Great Business Plan.
https://hbr.org/2017/07/how-to-write-a-great-business-plan
Harvard Business Review. (2021). Why Serial Entrepreneurs Are More Successful.
https://hbr.org/2021/06/why-serial-entrepreneurs-are-more-successful
HubSpot. (2024). Startup Statistics: The Ultimate List for 2024.
https://blog.hubspot.com/marketing/startup-stats
LinkedIn Talent Solutions. (2023). Startup Hiring Benchmarks Report.
https://business.linkedin.com/talent-solutions/resources/talent-strategy/startup-hiring-benchmarks
PitchBook. (2023). All In: Women in the VC Ecosystem 2023.
https://pitchbook.com/news/reports/2023-annual-us-vc-female-founders-dashboard
PitchBook. (2023). Global Venture Capital Report 2023.
https://pitchbook.com/news/reports/2023-annual-global-venture-report
PitchBook. (2025). Healthcare VC Trends Q1 2025.
https://pitchbook.com/news/reports/q1-2025-healthcare-vc-report
PwC. (2024). State of Climate Tech 2024.
https://www.pwc.com/gx/en/services/sustainability/publications/state-of-climate-tech.html
Rock Health. (2025). Digital Health Funding Report Q1 2025.
https://rockhealth.com/reports
Startup Genome. (2023). The Global Startup Ecosystem Report 2023.
https://startupgenome.com/report/gser2023
Statista. (2023). Healthcare Startup Revenue in the United States 2022.
https://www.statista.com/statistics/healthcare-startup-revenue-us
Statista. (2024). Artificial Intelligence Market Size 2024–2025.
https://www.statista.com/statistics/941835/artificial-intelligence-market-size-revenue-comparison
UK Government. (2024). Business Costs and Payroll Statistics.
https://www.gov.uk/government/collections/business-population-estimates
U.S. Bank. (2022). Small Business Failure Rates and Causes.
https://www.usbank.com/small-business/resources/business-failure-rates.html
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. (2023). Business Employment Dynamics: Entrepreneurship and Survival Rates by Industry.
https://www.bls.gov/bdm/entrepreneurship/entrepreneurship.htm
U.S. Small Business Administration. (2023). Small Business Finance and Investment Report.
 All Posts
All Posts


